
The depreciation expense is higher at the beginning and lower towards the end to reflect that most of the value has been used at the start. Under this method, the percentage of depreciation rate for each year is calculated by the years remaining in the useful life divided by the sum of remaining life every year throughout the asset’s life. The sum-of-the-years’ digits method is another variation on accelerated depreciation. Under this method, an asset’s depreciable base is multiplied by a declining rate. Calculate the sum of years’ digits depreciation for each year of the fixed asset above.
Hire An Accountant At The Most Affordable Prices
Accountingo.org aims to provide the best accounting and finance education for students, professionals, teachers, and business owners. Beth purchased a display shelf for her bakery costing $10,000 on 1 January 2020. The has a useful life of 4 years after which it is expected to have no residual value.
What is Qualified Business Income?
Companies purchase physical assets, also known as tangible assets as they add value to their business. Learn how to calculate your depreciable cost, the depreciable cost formula, and how Enerpize can help you calculate your depreciable. In the example above, your straight-line depreciation expense would have been $20,000 each year—$100,000 x 1 /5. Additionally, in later years, your depreciation deduction for this asset will be lower under the sum of the years’ digit method.
What is your current financial priority?
However, the company needs to properly allocate the cost so that the depreciation expense charged to the income statement matches the benefits that the company receives from the fixed assets. This is so that the recognition of the depreciation expense in the company’s accounting for investment in bonds account is properly in compliance with the matching principle of accounting. Sum of years is considered to be an accelerated method of calculating depreciation expense because it uses the highest depreciation rate at the beginning of an asset’s expected life.
Calculating Sum of the Years’ Digits Depreciation
The primary advantage of this method is that it provides a more accurate trend for Depreciation expenses. That is, the expense tends to be higher in early years, which makes sense if an asset gives up its benefits faster earlier on. From a conceptual perspective, these methods are most suited for assets that give up a greater portion of their benefits in their early years. This rate is a fraction, in which the numerator is the number of years remaining in the asset’s life at the beginning of the year and the denominator is the sum of the digits of the asset’s useful life. To find the delivery truck’s remaining useful life, we need to count it from the start of each year rather than the end. This may seem strange to you at first, but you will get the hang of it soon with practice.
- Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website.
- If you are a business owner, executive manager, or entrepreneur, you must understand what the depreciable cost is to account for business expenses correctly, timely, and compliantly.
- To calculate depreciation using the SYD formula, we need to input the remaining useful life of the asset at the start of the period (1 July 2021) which is 5 years.
- Industries such as technology, automotive, and manufacturing often benefit from this approach, as it aligns depreciation with the asset’s economic usefulness.
For example, if an asset has a useful life of 5 years, the sum of its years’ digits will equal 15 (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5). The asset has 3 years useful life at the end of which it is not expected to have any salvage value. However, Mega Coffee needs to pay $100,000 in shipping costs in order to move this massive order of computers across the country in due time. In addition, Mega Coffee is faced with a $400,000 installation charge to ensure that its computers are installed correctly and function at full capacity. Our example assumes ABC technologies that purchased computers for $4,000,000.
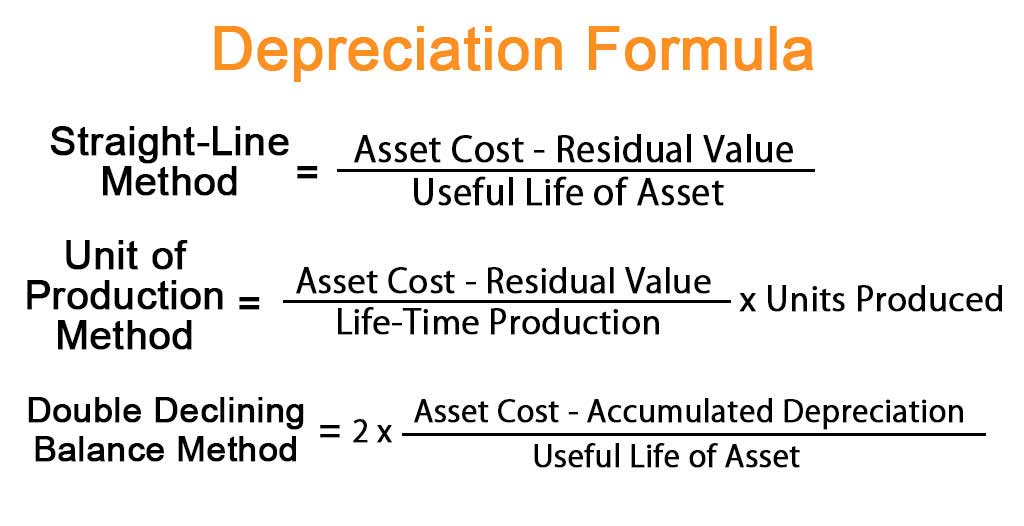
This means that the total amount of depreciation will be $150,000 spread over the equipment’s useful life of 5 years. While all the methods of depreciation would lead to the same result, the only variation is the time taken for depreciation recognition. The straight-line method may take much longer to calculate the depreciation expense.
The simplest and most common method of depreciation is the straight-line basis method of depreciation. The resulting number is then divided by the estimated useful life of the asset. Deskera Books is an online accounting software that your business can use to automate the process of journal entry creation and save time. The double-entry record will be auto-populated for each sale and purchase business transaction in debit and credit terms. Their values will automatically flow to respective financial reports.You can have access to Deskera’s ready-made Profit and Loss Statement, Balance Sheet, and other financial reports in an instant. The value of an asset comprises its acquisition cost plus additional costs such as maintenance, repairs, duties, re-prototyping, etc.
It must be noted that the final depreciation expense equals the salvage value of the asset. Enerpize is accounting-centric and, as such, is developed around accounting management needs. Undeniably, every business, big or small, must have an accounting system, manual or automated, to manage account needs end-to-end, expedite the reporting process, and stay compliant. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website.
Industries such as technology, automotive, and manufacturing often benefit from this approach, as it aligns depreciation with the asset’s economic usefulness. For example, a new model of a car or a piece of technology may become obsolete quickly, making accelerated depreciation advantageous. In the second accounting period ending on 31 December 2021, 9 months out of the first year of the asset overlaps as well as 3 months out of the asset’s second year. Therefore, the depreciation expense for the second accounting period is equal to 9/12 ✕ $4000 plus 3/12 ✕ $3000.